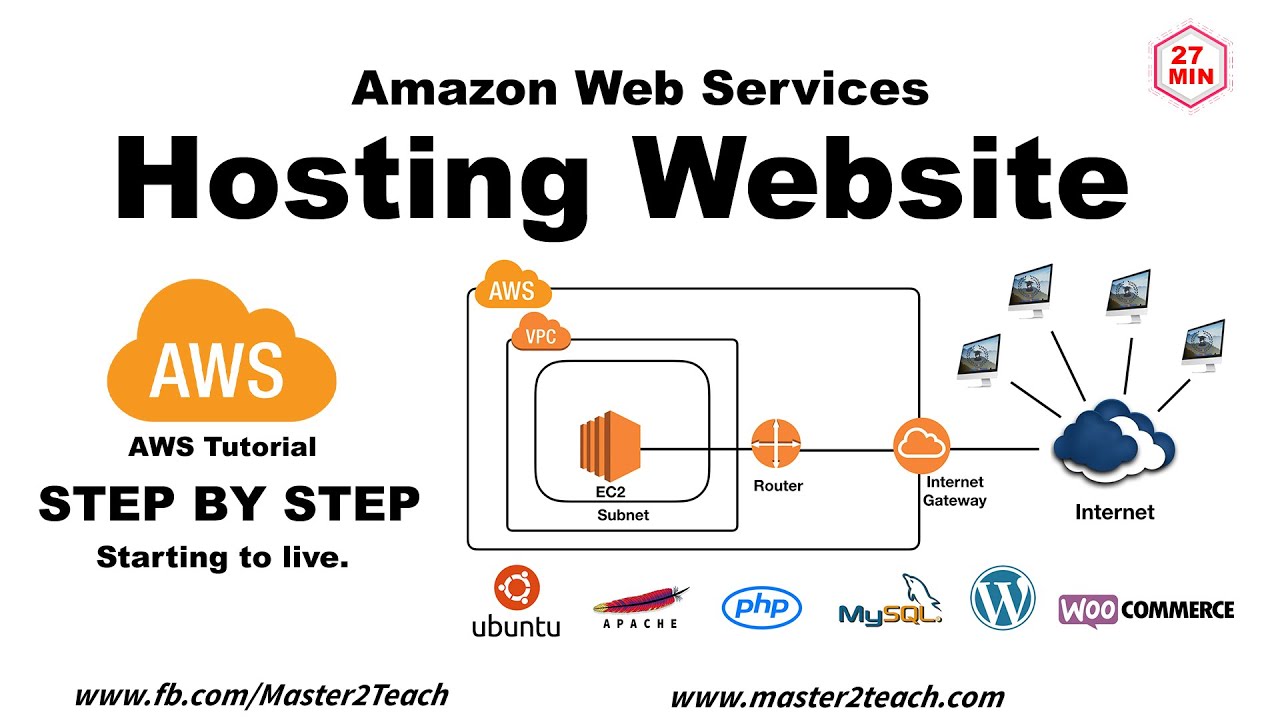
Virtual cloud servers have revolutionized the way businesses operate, offering a flexible and scalable alternative to traditional physical servers. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of virtual cloud servers, exploring their concepts, types, benefits, and practical applications.
From understanding the underlying technology to navigating the complexities of choosing the right provider, this guide provides valuable insights for individuals and organizations seeking to leverage the power of virtual cloud servers. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or a curious newcomer, this exploration aims to equip you with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions and unlock the full potential of virtual cloud servers.
Choosing the Right Virtual Cloud Server Provider

Choosing the right virtual cloud server provider is crucial for businesses of all sizes. The right provider can help you scale your infrastructure efficiently, reduce costs, and improve performance. However, with so many providers available, it can be challenging to determine which one is best for your needs.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Virtual Cloud Server Provider
When selecting a virtual cloud server provider, it’s important to consider several factors to ensure you choose the right fit for your business.
- Pricing: Different providers offer different pricing models. Some charge based on usage, while others charge a flat monthly fee. It’s essential to compare pricing models and choose one that aligns with your budget and anticipated usage.
- Features: The features offered by different providers vary. Some providers offer more advanced features, such as load balancing, auto-scaling, and disaster recovery. It’s essential to choose a provider that offers the features you need.
- Performance: The performance of a virtual cloud server is critical. You should choose a provider that offers high performance and low latency. Consider factors like network bandwidth, storage capacity, and CPU power.
- Security: Security is paramount when choosing a virtual cloud server provider. Look for a provider that offers robust security features, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption.
- Customer Support: It’s essential to have access to reliable customer support. Choose a provider that offers 24/7 support and has a proven track record of resolving issues promptly.
- Scalability: Your business needs will likely change over time. Choose a provider that offers scalability so you can easily adjust your resources as needed.
- Reputation: Before choosing a provider, research their reputation. Read reviews from other customers and assess their track record.
Comparing and Contrasting Different Providers
Once you’ve considered the factors mentioned above, you can start comparing different providers. Here’s a breakdown of some key areas to consider:
Pricing
- Pay-as-you-go: This model charges you based on your actual usage. It’s a good option if you have unpredictable usage patterns. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Reserved Instances: This model offers discounts for committing to a certain amount of usage for a set period. It’s a good option if you have predictable usage patterns.
- Spot Instances: This model allows you to bid on unused computing capacity. It’s a cost-effective option, but it comes with the risk of your instances being terminated if the price goes up.
Features
- Compute: Providers offer various compute options, such as virtual machines (VMs), containers, and serverless computing. Choose the option that best meets your application’s needs.
- Storage: Providers offer various storage options, including block storage, object storage, and file storage. Choose the option that provides the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness you need.
- Networking: Providers offer various networking options, including virtual private clouds (VPCs), load balancers, and content delivery networks (CDNs). Choose the option that provides the connectivity, security, and performance you need.
- Management Tools: Providers offer various management tools, such as dashboards, APIs, and command-line interfaces. Choose the tools that make it easy to manage your cloud infrastructure.
Customer Support
- Availability: Choose a provider that offers 24/7 support.
- Response Time: Choose a provider with a proven track record of resolving issues promptly.
- Channels: Choose a provider that offers multiple support channels, such as phone, email, and chat.
Checklist for Evaluating Potential Virtual Cloud Server Providers
To streamline your evaluation process, consider using a checklist. Here’s a sample checklist:
- Pricing:
- What are the provider’s pricing models?
- What are the costs associated with different services?
- Are there any discounts or promotions available?
- Features:
- What compute, storage, and networking options are available?
- What management tools are offered?
- Are there any security features included?
- Performance:
- What is the provider’s uptime guarantee?
- What is the average latency?
- How does the provider handle traffic spikes?
- Security:
- What security features are offered?
- What are the provider’s security certifications?
- What are the provider’s data privacy policies?
- Customer Support:
- What are the provider’s support hours?
- What support channels are available?
- What is the provider’s average response time?
- Scalability:
- How easily can you scale your resources up or down?
- What are the costs associated with scaling?
- Reputation:
- What is the provider’s track record?
- What do other customers say about the provider?
Security Considerations for Virtual Cloud Servers
Virtual cloud servers offer numerous benefits, including scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, these advantages come with inherent security challenges that require careful consideration. Understanding and mitigating these risks is crucial for ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of your data and applications.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a fundamental security measure that protects sensitive information from unauthorized access. Encrypting data at rest and in transit helps safeguard against data breaches, even if the underlying infrastructure is compromised.
- Encryption at rest: This involves encrypting data stored on virtual cloud servers, such as databases, files, and applications. Encryption keys should be securely managed and protected to prevent unauthorized decryption.
- Encryption in transit: This involves encrypting data transmitted between virtual cloud servers and other systems, such as client devices or other cloud services. Secure protocols like HTTPS and TLS should be used to ensure secure communication.
Access Control, Virtual cloud server
Access control mechanisms restrict access to virtual cloud servers and their resources, limiting who can access what and when. Implementing strong access control policies helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): RBAC assigns specific roles to users and grants them permissions based on their roles. This ensures that users only have access to the resources they need to perform their duties.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code from a mobile device.
- Least privilege principle: This principle dictates that users should only have access to the resources they need to perform their tasks. This minimizes the potential impact of a security breach.
Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating security vulnerabilities in virtual cloud servers and their associated software. Proactive vulnerability management helps prevent attacks by patching known vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Regular security scanning: Regularly scanning virtual cloud servers for vulnerabilities helps identify potential weaknesses and allows for timely remediation.
- Automated patching: Automating the patching process ensures that critical vulnerabilities are patched promptly, reducing the risk of exploitation.
- Security monitoring: Continuous security monitoring helps detect suspicious activity and potential breaches, allowing for rapid response and mitigation.
Future Trends in Virtual Cloud Server Technology
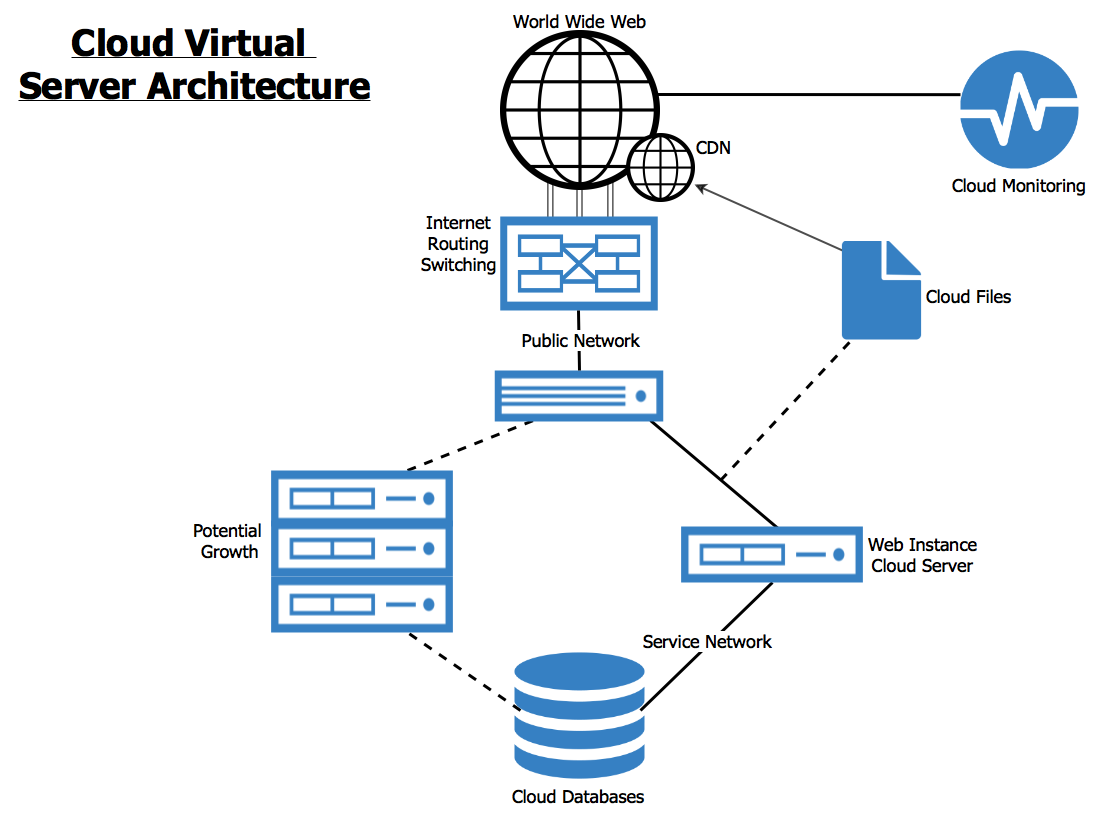
The realm of virtual cloud server technology is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in computing power, network infrastructure, and software development. These trends are shaping the future of how businesses and individuals interact with cloud computing.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing represents a significant shift in how applications are developed and deployed. In this paradigm, developers focus solely on writing code, without the need to manage underlying infrastructure. Cloud providers handle the provisioning, scaling, and maintenance of servers, allowing developers to concentrate on building innovative solutions.
Edge Computing
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the users, reducing latency and improving performance. As the volume of data generated by IoT devices and other connected systems explodes, edge computing offers a decentralized approach to processing and analyzing information in real-time.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming various aspects of cloud server technology. These technologies enable cloud providers to optimize resource allocation, predict demand fluctuations, and automate tasks. AI-powered security systems enhance the protection of virtual cloud servers, while ML algorithms improve the efficiency of data analytics and processing.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing holds the potential to revolutionize cloud server technology by offering exponentially faster processing capabilities. Quantum algorithms can solve complex problems that are intractable for classical computers, opening up new possibilities for scientific research, drug discovery, and financial modeling.
Increased Security and Compliance
As cloud adoption continues to grow, security and compliance become paramount. Cloud providers are investing heavily in advanced security measures, such as encryption, access control, and threat detection. Compliance with industry regulations like GDPR and HIPAA is also crucial for ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive data stored on virtual cloud servers.
Hybrid Cloud Solutions
Hybrid cloud solutions combine the benefits of public and private cloud environments, allowing organizations to leverage the best of both worlds. Businesses can use public cloud services for scalability and flexibility while maintaining sensitive data and applications on private cloud infrastructure.
Increased Use of Containers
Containers offer a lightweight and portable way to package and deploy applications. They provide a consistent environment across different platforms, simplifying the deployment and management of applications on virtual cloud servers.
Integration with Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology can enhance the security and transparency of cloud services. It provides a decentralized and immutable ledger for recording transactions, ensuring data integrity and preventing unauthorized access.
The Rise of Multi-Cloud Strategies
Organizations are increasingly adopting multi-cloud strategies, utilizing multiple cloud providers to diversify their infrastructure and avoid vendor lock-in. This approach offers greater flexibility and resilience, allowing businesses to optimize their cloud resources based on specific needs.
Closing Summary: Virtual Cloud Server
Virtual cloud servers have emerged as a transformative force in the digital landscape, offering a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes. As technology continues to evolve, virtual cloud servers will undoubtedly play an even more prominent role in shaping the future of computing, enabling innovation and driving efficiency across industries.