Server host, the backbone of your online presence, is the foundation upon which your website stands. It’s the digital space that houses your website’s files, making them accessible to visitors around the globe. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting your online journey, understanding server hosting is crucial to building a successful and reliable web presence.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of server hosting, exploring its different types, key features, and essential considerations for choosing the right plan. We’ll examine the factors that influence website performance, security, and scalability, empowering you to make informed decisions for your online success.
Server Hosting Basics
Server hosting is the process of providing and maintaining servers for websites, applications, and other online services. In essence, it’s like renting a virtual space where your website or application can live and be accessed by users on the internet.
Types of Server Hosting
Different types of server hosting cater to varying needs and budgets. The most common types are:
- Shared Hosting: In shared hosting, multiple websites share the resources of a single server. This is the most affordable option, suitable for basic websites with low traffic.
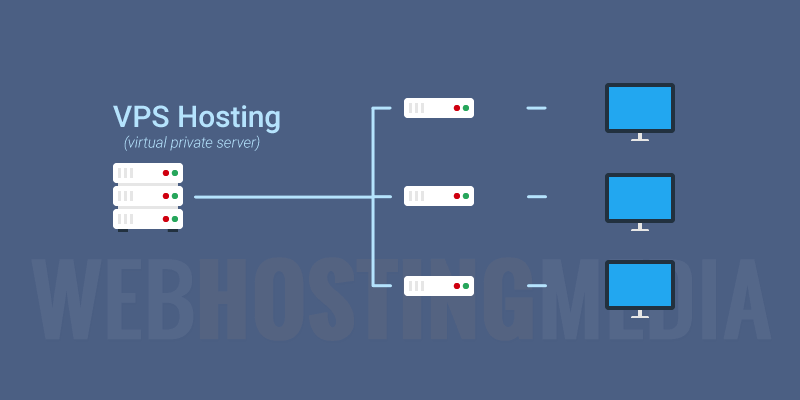
- VPS Hosting: VPS (Virtual Private Server) offers a virtualized environment on a physical server, providing dedicated resources and greater control. It’s a step up from shared hosting, suitable for websites with moderate traffic and resource demands.
- Dedicated Hosting: With dedicated hosting, you have an entire server dedicated solely to your website or application. This provides maximum performance and security, ideal for high-traffic websites or applications with demanding resource requirements.
- Cloud Hosting: Cloud hosting utilizes a network of servers to distribute resources and provide scalability. It’s flexible and adaptable, suitable for websites with fluctuating traffic and dynamic resource needs.
Popular Server Hosting Providers
Several reputable server hosting providers offer a range of solutions to meet diverse needs. Here are a few popular examples:
- GoDaddy: Known for its user-friendly interface and wide range of hosting plans, GoDaddy is a popular choice for beginners.
- Bluehost: Another well-established provider, Bluehost offers reliable and affordable hosting solutions, particularly for WordPress websites.
- HostGator: HostGator is known for its competitive pricing and excellent customer support. They provide a variety of hosting options, including shared, VPS, and dedicated hosting.
- DigitalOcean: A popular choice for developers and businesses seeking more control and flexibility, DigitalOcean offers cloud-based VPS hosting with robust features and scalability.
- AWS (Amazon Web Services): A leading cloud computing platform, AWS offers a wide range of server hosting options, including EC2 instances, Elastic Beanstalk, and Lambda functions.
Choosing the Right Hosting Plan
Choosing the right server hosting plan is crucial for the success of any website or application. It’s like picking the right vehicle for a journey – you need to consider the destination, the load you’ll carry, and your budget to make the best choice.
Factors to Consider, Server host
The right hosting plan depends on several factors, including:
- Traffic: How many visitors do you expect your website to receive? If you anticipate a large number of visitors, you’ll need a hosting plan with sufficient bandwidth and resources to handle the traffic.
- Storage: How much storage space do you need for your website files, databases, and other data? The size of your website, the number of images and videos, and the complexity of your application will all impact your storage requirements.
- Resources: How much processing power (CPU), memory (RAM), and other resources will your website or application need to function smoothly? The more complex your website or application, the more resources you’ll require.
- Budget: How much are you willing to spend on hosting? There are a wide range of hosting plans available, from budget-friendly options to premium plans with advanced features.
Types of Hosting
There are various types of hosting, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
- Shared Hosting: This is the most affordable option, where multiple websites share the same server resources. It’s suitable for small websites with low traffic and minimal resource needs. However, shared hosting can be slow and unreliable if other websites on the server experience high traffic.
- VPS Hosting: Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting provides a dedicated portion of a server’s resources, offering more control and performance than shared hosting. It’s a good choice for websites with moderate traffic and resource requirements.
- Dedicated Hosting: Dedicated hosting gives you an entire server exclusively for your website. This offers the highest level of performance, security, and control, but it’s also the most expensive option.
- Cloud Hosting: Cloud hosting distributes your website across multiple servers, providing scalability and flexibility. It’s ideal for websites with unpredictable traffic and resource demands.
Choosing the Right Plan
Here are some tips for choosing the most suitable hosting plan for your specific needs:
- Estimate your website traffic: Analyze your website’s current traffic or use tools like Google Analytics to predict future traffic growth.
- Assess your storage needs: Consider the size of your website files, databases, and other data. You can use online tools to estimate your storage requirements.
- Determine your resource needs: Analyze your website’s performance and identify potential bottlenecks. Consider the complexity of your website or application and the resources it requires.
- Compare hosting providers: Research different hosting providers and compare their features, pricing, and customer support. Look for reviews and testimonials from other users.
- Start with a basic plan and scale up as needed: You can always upgrade your hosting plan later if your website’s traffic or resource demands increase.
Server Hosting Features
Choosing the right server hosting plan involves understanding the various features available. These features are essential for optimizing website performance, ensuring security, and facilitating growth.
Control Panel
A control panel is a user-friendly interface that allows you to manage your server and website. It simplifies tasks such as creating email accounts, managing databases, installing applications, and configuring security settings. Popular control panels include cPanel, Plesk, and DirectAdmin.
Security
Website security is paramount. Server hosting providers offer various security features to protect your website from threats such as malware, hacking attempts, and data breaches. These features include:
- Firewalls: Act as a barrier between your server and the internet, blocking unauthorized access and malicious traffic.
- Anti-virus software: Scans your server for malware and removes any detected threats.
- SSL certificates: Encrypt data transmitted between your website and visitors, ensuring secure communication and protecting sensitive information.
- Regular security updates: Ensure your server software is up-to-date with the latest security patches and fixes.
Backups
Data loss can be devastating. Server hosting providers offer backup solutions to safeguard your website’s data.
- Automatic backups: Regularly create copies of your website’s files and databases, ensuring data recovery in case of accidents or disasters.
- Offsite backups: Store backups in a separate location, protecting them from server failures or physical damage.
- Backup restoration: Allow you to easily restore your website from a backup in case of data loss.
Scalability
As your website grows, you may need to increase its resources to handle increased traffic and demand. Scalable hosting solutions allow you to adjust your server’s resources, such as CPU, RAM, and storage, on demand. This ensures your website remains responsive and performs well even during peak traffic periods.
Website Performance Optimization
Website performance plays a crucial role in user experience and search engine ranking. Server hosting can significantly impact website speed and responsiveness.
- Server location: Choosing a server location close to your target audience can reduce latency and improve website speed.
- Server resources: Adequate CPU, RAM, and storage capacity ensure your website runs smoothly and handles traffic efficiently.
- Caching: Store frequently accessed website data in temporary storage, reducing server load and improving page loading times.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): Distribute website content across multiple servers globally, reducing loading times for visitors from different locations.
Essential Features for Different Website Types
- E-commerce websites: Require secure payment gateways, robust shopping cart functionality, and sufficient resources to handle high traffic volumes.
- Blogs: Need a content management system (CMS) for easy post creation and editing, and sufficient bandwidth to accommodate media files and images.
- Portfolios: Often prioritize visual appeal and performance, requiring fast loading times and high-quality image hosting.
Server Hosting Costs

Choosing the right server hosting plan can be a significant decision for businesses and individuals alike. It’s essential to understand the cost structure and compare different providers to find the best value for your needs.
Cost Structure of Server Hosting Plans
The cost of server hosting plans varies based on several factors, including the type of hosting, resources allocated, and additional services. Here’s a breakdown of the typical cost components:
* Monthly Fees: This is the primary cost of server hosting. The monthly fee is determined by the hosting plan’s features and resources, such as storage space, bandwidth, and processing power.
* Additional Services: Many hosting providers offer additional services for an extra cost, such as domain registration, SSL certificates, website backups, and security features.
* Scalability: As your website traffic grows, you might need to upgrade your hosting plan. Scalability refers to the ability to increase resources and pay a higher monthly fee accordingly.
Comparing Pricing Models of Hosting Providers
Different hosting providers use various pricing models. Here are some common models:
* Pay-as-you-go: This model allows you to pay only for the resources you use. It’s ideal for websites with fluctuating traffic and can be cost-effective if you only need occasional bursts of resources.
* Fixed monthly fee: This model offers a predictable monthly cost for a set amount of resources. It’s suitable for websites with consistent traffic and predictable resource needs.
* Tiered pricing: This model offers different pricing tiers based on the resources included in each plan. It allows you to choose a plan that best suits your current needs and budget.
Comparing Hosting Plans from Various Providers
The following table compares hosting plans from different providers, including their features and costs.
| Provider | Plan | Storage | Bandwidth | CPU Cores | Monthly Fee | Features |
|—|—|—|—|—|—|—|
| Provider A | Basic | 10 GB | 100 GB | 1 | $5 | Basic website hosting |
| | Standard | 25 GB | 250 GB | 2 | $10 | Enhanced features |
| | Premium | 50 GB | 500 GB | 4 | $20 | Advanced features |
| Provider B | Starter | 5 GB | 50 GB | 1 | $3 | Basic website hosting |
| | Pro | 15 GB | 150 GB | 2 | $7 | Enhanced features |
| | Enterprise | 30 GB | 300 GB | 4 | $15 | Advanced features |
| Provider C | Shared | 1 GB | 10 GB | 1 | $1 | Shared hosting |
| | Cloud | 10 GB | 100 GB | 2 | $5 | Cloud hosting |
| | Dedicated | 50 GB | 500 GB | 4 | $15 | Dedicated server |
Note: The pricing and features in this table are for illustrative purposes only and may vary depending on the specific provider and plan.
Server Hosting Security
In the digital landscape, where data is paramount, ensuring server security is crucial for website owners and businesses alike. Server security threats can have severe consequences, ranging from website downtime and data breaches to financial losses and reputational damage. Understanding common threats and implementing robust security measures is essential for safeguarding your online presence.
Common Server Security Threats
Server security threats can come in various forms, each posing unique challenges.
- Malware: Malicious software, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans, can infiltrate servers and compromise data integrity, steal sensitive information, or disrupt website functionality.
- DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm servers with a flood of traffic, rendering websites inaccessible to legitimate users. These attacks can cripple online businesses and cause significant financial losses.
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data, such as customer information, financial records, or proprietary data, can lead to severe consequences, including legal repercussions, financial losses, and reputational damage.
How Server Hosting Providers Contribute to Website Security
Server hosting providers play a vital role in safeguarding websites by implementing various security measures.
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier, blocking unauthorized access to servers and preventing malicious traffic from entering the network.
- Anti-Malware Software: Hosting providers often deploy anti-malware software to detect and remove malware threats before they can compromise servers.
- Regular Security Updates: Server operating systems and software applications require regular security updates to patch vulnerabilities and prevent exploitation by attackers.
- Data Backups: Hosting providers often offer data backup services, allowing website owners to restore data in case of a security breach or data loss.
- Security Monitoring: Hosting providers often monitor servers for suspicious activity and promptly respond to potential security threats.
Enhancing Website Security Through Server Configuration and Practices
Website owners can further enhance their website security by implementing server configuration and best practices.
- Strong Passwords: Using strong, unique passwords for all website accounts, including administrative panels, is crucial for preventing unauthorized access.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Implementing two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of authentication, such as a password and a code sent to their mobile device.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits helps identify vulnerabilities and potential threats that may have been overlooked.
- Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP): Using SFTP for transferring files between your local computer and the server ensures secure data transmission.
- HTTPS Encryption: Enabling HTTPS encryption ensures secure communication between the server and the user’s browser, protecting sensitive data from interception.
- Website Security Plugins: Installing and configuring website security plugins can provide additional protection against malware, brute-force attacks, and other threats.
- Regularly Update Software: Keeping website software, including plugins and themes, updated is essential for patching security vulnerabilities and preventing exploitation by attackers.
Server Hosting for Different Applications
Server hosting is a fundamental aspect of website and application development, providing the infrastructure necessary to run and deliver content to users. Different applications have distinct requirements, demanding specific hosting solutions to ensure optimal performance, security, and scalability.
WordPress Hosting
WordPress, a popular content management system (CMS), powers a significant portion of websites worldwide. WordPress hosting offers specialized features tailored to the platform’s needs, including:
- One-click WordPress installation: Simplifies the setup process, allowing users to quickly install WordPress with a few clicks.
- Optimized performance: WordPress hosting providers often employ caching mechanisms and other performance-enhancing techniques to ensure fast loading times.
- Security features: Robust security measures, such as malware scanning and firewall protection, are essential to safeguard WordPress websites from attacks.
- Automatic updates: WordPress hosting providers typically handle automatic updates for the WordPress core, plugins, and themes, minimizing security vulnerabilities.
Database Hosting
Databases are essential for storing and managing large amounts of data, powering applications such as e-commerce platforms, social media sites, and content management systems. Database hosting provides dedicated resources and tools for managing databases effectively:
- Database management systems (DBMS): Popular DBMS options include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB, each offering distinct features and capabilities.
- Database backups and recovery: Regular backups and efficient recovery mechanisms are crucial to protect valuable data from loss or corruption.
- Performance optimization: Database hosting providers offer tools and strategies to optimize database performance, ensuring fast query execution and efficient data access.
- Security measures: Database hosting includes security features like user authentication, access control, and encryption to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Web Application Hosting
Web applications, such as online stores, social media platforms, and business software, require hosting solutions that can handle complex functionalities and dynamic content. Web application hosting provides:
- Scalability and flexibility: Web application hosting solutions can scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance even during peak traffic periods.
- Programming language support: Web application hosting supports various programming languages, frameworks, and technologies, including PHP, Python, Node.js, and Ruby on Rails.
- Integration with third-party services: Web application hosting providers often offer seamless integration with essential services like payment gateways, email marketing platforms, and analytics tools.
- Monitoring and support: Web application hosting provides comprehensive monitoring and support services to ensure application stability and address technical issues promptly.
Hosting Options for Different Application Types
| Application Type | Best Hosting Options | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| WordPress Websites | WordPress Hosting, Shared Hosting | Performance, Security, Ease of Use |
| E-commerce Websites | VPS Hosting, Dedicated Hosting | Scalability, Performance, Security |
| High-Traffic Websites | Cloud Hosting, Dedicated Hosting | Scalability, Performance, Reliability |
| Database-Intensive Applications | Database Hosting, VPS Hosting | Database Performance, Security, Backup & Recovery |
| Web Applications | Cloud Hosting, VPS Hosting, Dedicated Hosting | Scalability, Performance, Programming Language Support |
Server Hosting for Businesses
Server hosting is a crucial aspect of modern business operations, providing a reliable and scalable platform for websites, applications, and data storage. By choosing the right server hosting solution, businesses can unlock significant benefits, including improved performance, enhanced security, and increased flexibility to adapt to evolving needs.
Benefits of Server Hosting for Businesses
Server hosting offers a range of advantages that can significantly impact business success. Here are some key benefits:
- Reliability: Server hosting ensures consistent uptime and availability, minimizing downtime and disruptions to business operations. Dedicated servers offer higher levels of reliability compared to shared hosting, as resources are not shared with other websites.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, their infrastructure needs to adapt. Server hosting provides the flexibility to scale resources up or down as required, ensuring that the hosting environment can accommodate increasing traffic and data demands.
- Security: Server hosting provides enhanced security measures to protect sensitive business data. Dedicated servers offer greater control over security configurations and allow businesses to implement stricter security protocols.
Supporting Business Growth and Expansion
Server hosting plays a vital role in supporting business growth and expansion by:
- Enabling new business opportunities: Server hosting allows businesses to launch new websites, applications, and services, expanding their reach and market presence.
- Facilitating global expansion: Server hosting solutions with global data centers enable businesses to reach customers in different regions, reducing latency and improving user experience.
- Providing a platform for innovation: Server hosting provides a stable and scalable platform for businesses to experiment with new technologies, develop innovative applications, and stay ahead of the competition.
Examples of Businesses Leveraging Server Hosting
Many businesses across various industries leverage server hosting to power their operations:
- E-commerce businesses: Server hosting provides the necessary infrastructure to handle high volumes of traffic, secure online transactions, and store customer data.
- Software companies: Server hosting enables software companies to host their applications, provide updates and support, and manage user accounts.
- Financial institutions: Server hosting is critical for financial institutions to manage sensitive data, process transactions securely, and maintain regulatory compliance.
- Healthcare providers: Server hosting enables healthcare providers to store patient records securely, manage electronic health records, and facilitate telehealth services.
Server Hosting Trends
The server hosting landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing user demands. Emerging trends are reshaping how businesses and individuals access and manage computing resources. Understanding these trends is crucial for making informed decisions about server hosting choices.
Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting is a dominant trend in server hosting, offering a flexible and scalable approach to managing computing resources. Instead of relying on physical servers, cloud hosting utilizes a network of data centers to provide on-demand access to resources like servers, storage, and software.
- Increased Flexibility and Scalability: Cloud hosting allows businesses to scale their resources up or down as needed, adapting to fluctuating workloads and seasonal demands. This flexibility helps optimize resource utilization and reduce costs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By paying only for the resources they use, businesses can significantly reduce their infrastructure costs compared to traditional on-premises servers. Cloud providers offer pay-as-you-go models, eliminating upfront investments and ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Enhanced Security and Reliability: Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures and redundancy, ensuring data protection and service availability. This reduces the burden on businesses to manage security and infrastructure maintenance.
Edge Computing
Edge computing is gaining traction as a solution for latency-sensitive applications and data processing closer to users. It involves deploying computing resources at the network edge, near the source of data, to reduce latency and improve response times.
- Reduced Latency: By processing data closer to users, edge computing minimizes the distance data travels, resulting in faster response times and improved user experience. This is particularly beneficial for real-time applications like online gaming, video streaming, and IoT devices.
- Enhanced Performance: Edge computing distributes processing power across the network, reducing the load on centralized servers and improving overall application performance. This is crucial for handling large volumes of data and supporting demanding applications.
- Improved Data Locality: Edge computing allows data to be processed and stored locally, reducing the need for data transfer to centralized data centers. This enhances data privacy and security, as sensitive information remains within the user’s geographical region.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is a revolutionary approach to server hosting, where developers can run code without managing servers or infrastructure. Cloud providers handle all the underlying infrastructure, allowing developers to focus solely on writing and deploying code.
- Simplified Development and Deployment: Serverless computing eliminates the need for server management, simplifying the development process and reducing deployment time. Developers can focus on writing code without worrying about infrastructure complexities.
- Automatic Scaling: Serverless platforms automatically scale resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and eliminating the need for manual scaling. This provides a cost-effective solution for handling fluctuating workloads.
- Pay-per-Use Pricing: Serverless computing follows a pay-per-use model, where users are charged only for the resources they consume. This eliminates the need for upfront investments and reduces operational costs.
Server Hosting Alternatives

While traditional server hosting remains a popular choice, the emergence of cloud computing and other technologies has opened up a range of alternative options that offer unique advantages and cater to diverse needs. These alternatives provide greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional server hosting.
Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting is a popular alternative to traditional server hosting, offering a virtualized environment where resources are shared across multiple servers. This allows businesses to access computing power and storage on demand, eliminating the need for upfront investments in physical infrastructure.
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of cloud hosting:
- Advantages:
- Scalability: Cloud hosting allows businesses to easily scale their resources up or down as needed, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
- Cost-effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go pricing models make cloud hosting more affordable, especially for businesses with fluctuating resource requirements.
- Flexibility: Cloud hosting offers a wide range of services, including virtual machines, databases, and storage solutions, providing businesses with the flexibility to choose the services that best suit their needs.
- High Availability: Cloud providers typically offer multiple data centers and redundancy measures, ensuring high availability and minimal downtime.
- Easy Management: Cloud platforms provide user-friendly interfaces and tools for managing resources and applications.
- Disadvantages:
- Security Concerns: Security is paramount in cloud environments, and businesses must carefully choose reputable providers and implement robust security measures.
- Vendor Lock-in: Switching cloud providers can be challenging and may involve data migration and configuration changes.
- Internet Dependency: Cloud hosting relies heavily on internet connectivity, which can impact performance and availability during outages.
Businesses are increasingly leveraging cloud hosting to manage their web presence. For example, a rapidly growing e-commerce company can use cloud hosting to scale their infrastructure to accommodate peak traffic during promotional periods. They can easily add more servers and storage space as needed, ensuring smooth operations and a positive customer experience.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
Content delivery networks (CDNs) are distributed networks of servers that cache and deliver website content to users from locations closer to them. This significantly reduces latency and improves website performance, particularly for users located far from the origin server.
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of using CDNs:
- Advantages:
- Improved Performance: CDNs reduce latency and improve website loading times, enhancing user experience and increasing conversion rates.
- Increased Scalability: CDNs can handle large volumes of traffic, ensuring website availability even during peak periods.
- Enhanced Security: CDNs offer security features like DDoS protection and SSL encryption, safeguarding websites from attacks.
- Reduced Bandwidth Costs: CDNs can significantly reduce bandwidth costs by caching content closer to users, minimizing data transfer from the origin server.
- Disadvantages:
- Cost: CDNs can be expensive, especially for websites with high traffic volumes.
- Complexity: Implementing and managing CDNs can be complex, requiring technical expertise.
- Limited Control: Businesses may have limited control over the caching and delivery of content, relying on the CDN provider’s policies and configurations.
CDNs are widely used by businesses with global reach. For example, a media streaming service can use a CDN to deliver high-quality video content to users worldwide, ensuring a seamless viewing experience regardless of their location.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is a cloud-based execution model where code runs in response to events without the need for explicit server management. It allows developers to focus on writing code while the cloud provider handles all infrastructure and scaling needs.
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of serverless computing:
- Advantages:
- Cost-effectiveness: Pay-per-execution pricing makes serverless computing cost-effective, especially for applications with sporadic or unpredictable workloads.
- Scalability: Serverless platforms automatically scale resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance without manual intervention.
- Focus on Code: Developers can focus on writing code without managing infrastructure, leading to faster development cycles.
- High Availability: Serverless platforms typically offer high availability and redundancy, ensuring application uptime.
- Disadvantages:
- Cold Starts: Serverless functions can experience cold starts, where initial executions take longer due to the need to provision resources.
- Vendor Lock-in: Switching serverless providers can be challenging due to platform-specific features and dependencies.
- Debugging Challenges: Debugging serverless functions can be complex due to the distributed nature of the execution environment.
Serverless computing is gaining popularity for applications like API endpoints, event processing, and real-time data analysis. A social media platform, for example, can use serverless functions to handle user interactions, notifications, and data processing, scaling resources dynamically based on user activity.
Final Thoughts
As the digital landscape evolves, server hosting continues to play a vital role in shaping the future of the internet. By understanding the fundamentals of server hosting, you can navigate the complexities of the online world with confidence, ensuring a smooth and efficient experience for both you and your visitors. Whether you’re building a personal blog, launching an e-commerce store, or powering a complex web application, server hosting provides the foundation for your online success.
A server host is a powerful tool for managing various services, including the efficient handling of data and applications. One such service is a print server , which centralizes printing tasks and allows users to print documents from any device connected to the network.
By hosting a print server, you can streamline your printing workflow and optimize resource allocation for your server host.